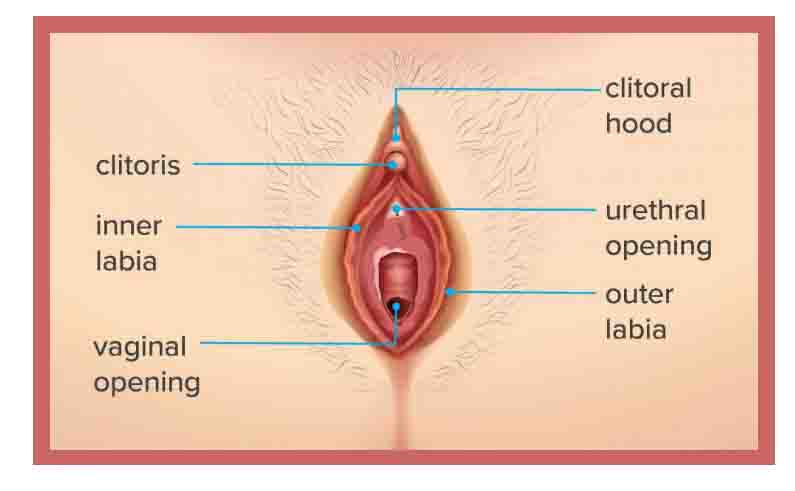
Gene Flow
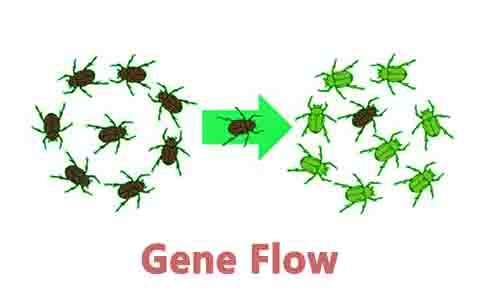
Gene Flow Definition The exchange of alleles between two or more populations is known as gene flow. In some cases, it is referred to as gene flow or allele migration. Despite the fact that migrating animals often carry new alleles from one population to another, gene flow cannot occur unless they interbreed with the new … Read more